Join us as we delve into Infrastructure Security, where we specialise in fortifying your digital assets with cutting-edge solutions. Let’s explore the crucial elements of infrastructure security, our comprehensive approach to protection, and the transformative benefits it brings to your organisation.
Introduction to IT Infrastructure Security
Infrastructure Security refers to the measures and protocols put in place to protect the underlying components of your IT environment, including networks, servers, databases, and applications. It encompasses a range of practices aimed at preventing unauthorised access, detecting and responding to threats, and ensuring the integrity and availability of your critical systems and data.
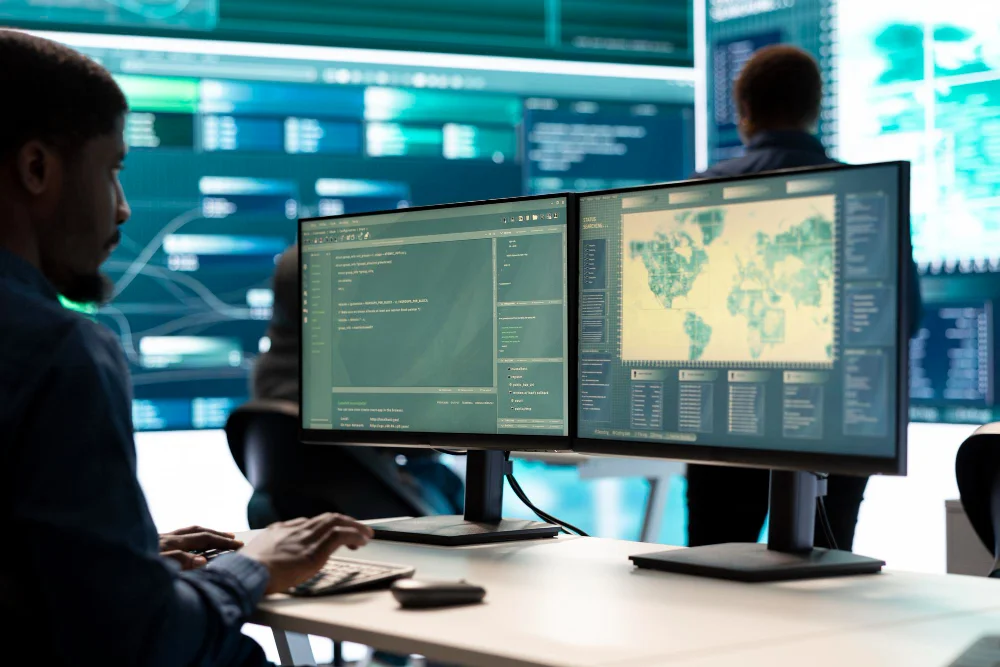

Securing 7 Key Components of Your Infrastructure
Network Security
Endpoint Security
Server Security
Database Security
Application Security
Cloud Security
Physical Security
Risk Mitigation
Infrastructure security helps mitigate the risk of data breaches, financial losses, and reputational damage associated with cyber threats.
Regulatory Compliance
Compliance with industry regulations and data protection laws such as GDPR, HIPAA, and PCI DSS is facilitated through robust infrastructure security practices.
Business Continuity
Ensuring the availability and reliability of critical systems and data, even in the face of security incidents or disruptions, promotes business continuity and resilience.
Cost Savings
Proactively investing in infrastructure security can lead to cost savings by reducing the likelihood and impact of security incidents, minimising downtime, and avoiding regulatory fines.
Levels of Infrastructure Security
Preventive Security Measures
Detective Security Measures
Corrective Security Measures
Benefits of Infrastructure Security


Firewalls
Intrusion Detection/Prevention Systems (IDS/IPS)
Vulnerability Scanners
Get Your Free Audit Now!
Frequently asked questions
What is infrastructure security?
Why is cloud infrastructure security important?
What practices are involved in cloud infra security?
How can I ensure secure cloud infrastructure?
What are the key components of a cloud security infrastructure?
What is infrastructure security in cloud environments?
How do you build a secure cloud infrastructure?
What are the benefits of cloud infrastructure security?
How does cloud infra security differ from traditional IT security?
What role do infrastructure security protocols play in cloud environments?
Client Testimonials












